Barcode Guide
Japanese Post 4-State Customer Code
Japanese Post was created for the Japanese postal system to encode addresses on mail for faster automatic processing.
The symbol comprises the following elements:
-
Start bars: The first two bars are the start bars. Together with the stop bars, they determine the orientation of the barcode symbol. They always have the values 1 and 3, respectively.
-
New Postal Number Code: This field is seven characters (21 bars) long.
-
Address Indication number: This field is 13 characters (39 bars) long. If the address does not require the full set of characters, filler characters are used.
-
Check digit: This field is three bars long and is always located just before the stop bars.
-
Stop bars: The last two bars. Together with the start bars, they determine the orientation of the barcode symbol. They always have the values 3 and 1, respectively.
In addition, Japanese Post 4-State Customer Code requires a quiet zone space of at least 2 mm on all sides.
The bars in each symbol are separated into fields that represent characters. Each character is made up of three bars. The following diagram shows each field and its function.

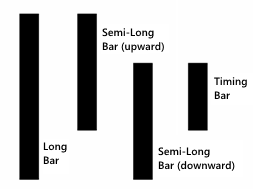
The term "4-state" is derived from the fact that each bar in this symbology is in one of four states, each of which has its own numerical value. The names of the four states and their corresponding values are as follows:
-
Long bar, value = 1
-
Semi-long bar (upward), value = 2
-
Semi-long bar (downward), value = 3
-
Timing bar, value = 4
These are illustrated in the following diagram.
This symbology supports the following alphanumeric characters:
Numbers and the hyphen character are represented by single three-bar characters. Letters are represented by a combination of a numeral and a control character (CC) as follows:
-
A-J use CC1
-
K-T use CC2
-
U-Z use CC3
Priority Codes are CC4 for normal priority and CC7 for highest priority.
To correctly position a Japanese Post barcode, it must be printed parallel to one edge of the piece of mail either horizontally or vertically. The barcode must also be within the following margins:
Other things to consider when you position your barcodes include the following:
-
No part of the barcode may appear in the canceling and metering zone. The metering zone is 35 mm from the top edge and 70 mm from the right edge.
-
The angle of inclination of the barcode with respect to the barcode's axis and the parallel edge of the piece of mail should be within 5 degrees.
-
The preferred position of the barcode is below the written address if horizontal. If the address is vertical, the barcode can be printed to the right, to the left, or at the bottom of the address.
A Japanese Post barcode requires two data input values: Postal Code and Address Indication. For example, a typical Japanese address such as the following would have a Postal Code value of 170-3293 and an Address Indication value of 5-2-1: