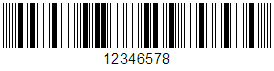Telepen
Telepen was developed in 1972 by SB Electronic Systems Ltd. in the United Kingdom. It is a continuous, variable-length, one-dimensional symbology that is designed to encode all 128 ASCII characters without using shift characters and to be highly reliable even when printed by ordinary printers that are not intended for barcode printing. Telepen was intended to be a competitor to Code 128 and Code 93. Its main use has been in university and other academic libraries in the UK.
Telepen offers a compressed numeric mode that has twice the density of the standard mode. Switching between modes is supported one time per symbol.
Telepen is defined in the AIM Europe Telepen Uniform Symbology Specification standard and is further described in the SB Electronic Systems Telepen - Barcode Symbology Information and History document.
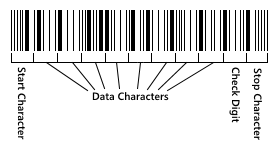
The symbol comprises the following elements:
-
Leading quiet zone
-
Start character (an underscore [_])
-
One or more data characters
-
Check digit
-
Stop character (lowercase z)
-
Trailing quiet zone
Each character is 16 modules wide and is made up of between four and eight bars and spaces, each of which is either one or three modules wide. The data characters encode 8 bits with even parity. In numeric-only applications, each character can encode two digits.
Elements within a character are read with the least significant digit on the left.
For the start character, the Telepen documentation specifies binary 01011111, which is the ASCII underscore character (_). The start character consists of five narrow bar and narrow space pairs followed by one wide bar and wide space pair.
The stop character is 11111010, which is the ASCII "z" character. The stop character consists of one wide bar and wide space pair followed by five narrow bar and narrow space pairs.
The AIM specification for Telepen describes two other start and stop character sets, which indicate to the reader that the symbol contains compressed numeric data.
Telepen requires a minimum quiet zone width of 10X or 2.54 mm, whichever is greater.
This symbology supports all 128 lower ASCII characters as binary data. No shift character is needed.
In numeric-only applications, this symbology supports all numeric digits (0-9).
Telepen contains a check digit that is based on the modulo 127 (mod 127) algorithm. In space-constrained symbols, a modulo 11 check digit can be used instead.
Telepen symbols can encode up to eight ASCII characters per inch or 16 digits per inch in numeric-only applications. Every character takes the same amount of space, so barcode length will not vary unless the data length itself varies.